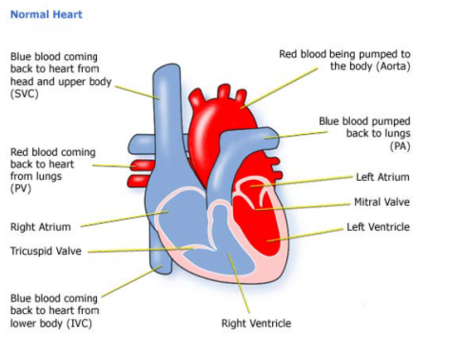
Blood is pumped through your heart in only one direction. Heart valves play a key role in this one-way blood flow, opening and closing with each heartbeat. Pressure changes on either side of the valves cause them to open their flap-like "doors" (called cusps or leaflets) at just the right time, then close tightly to prevent a backflow of blood.
There are 4 valves in the heart:
- Tricuspid valve
- Pulmonary valve
- Mitral valve
- Aortic valve
Nearly all of these operations are done to repair or replace the mitral or aortic valves. These valves are on the left side of the heart, which works harder than the right. They control the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the rest of the body.
Valve Disease
If valve damage is mild, doctors may be able to treat it with medicines. If damage to the valve is severe, surgery to repair or replace the valve may be needed.
What is valve repair?
Valve repair can usually be done on congenital valve defects (defects you are born with) and has a good success record with treating mitral valve defects.
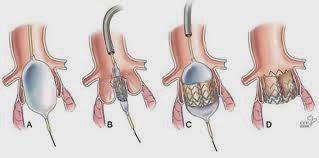
Here are some procedures surgeons may use to repair a valve:
- Commissurotomy, which is used for narrowed valves, where the leaflets are thickened and perhaps stuck together. The surgeon opens the valve by cutting the points where the leaflets meet.
- Valvuloplasty, which strengthens the leaflets to provide more support and to let the valve close tightly. This support comes from a ring-like device that surgeons attach around the outside of the valve opening.
- Reshaping, where the surgeon cuts out a section of a leaflet. Once the leaflet is sewn back together, the valve can close properly.
- Decalcification, which removes calcium buildup from the leaflets. Once the calcium is removed, the leaflets can close properly.
- Repair of structural support, which replaces or shortens the cords that give the valves support (these cords are called the chordae tendineae and the papillary muscles). When the cords are the right length, the valve can close properly.
- Patching, where the surgeon covers holes or tears in the leaflets with a tissue patch.
What is valve replacement?
Severe valve damage means that the valve will need to be replaced. Valve replacement is most often used to treat aortic valves and severely damaged mitral valves. It is also used to treat any valve disease that is life-threatening. Sometimes, more than one valve may be damaged in the heart, so patients may need more than one repair or replacement.
There are 2 kinds of valves used for valve replacement:
- Mechanical valves, which are usually made from materials such as plastic, carbon, or metal. Mechanical valves are strong, and they last a long time. Because blood tends to stick to mechanical valves and create blood clots, patients with these valves will need to take blood-thinning medicines for the rest of their lives.
- Biological valves, which are made from animal tissue (called a xenograft) or taken from the human tissue of a donated heart (called an allograft or homograft). Sometimes, a patient's own tissue can be used for valve replacement (called an autograft). Patients with biological valves usually do not need to take blood-thinning medicines. These valves are not as strong as mechanical valves, though, and they may need to be replaced every 10 years or so. Biological valves break down even faster in children and young adults, so these valves are used most often in elderly patients.
You and your doctor will decide which type of valve is best for you.
During valve repair or replacement surgery, the breastbone is divided, the heart is stopped, and blood is sent through a heart-lung machine. Because the heart or the aorta must be opened, heart valve surgery is open heart surgery.
What to Expect
The operation will usually be scheduled at a time that is best for you and your surgeon, except in urgent cases. As the date of your surgery gets closer, be sure to tell your surgeon and cardiologist about any changes in your health. If you have a cold or the flu, this can lead to infections that may affect your recovery. Be aware of fever, chills, coughing, or a runny nose. Tell the doctor if you have any of these symptoms.
Also, remind your cardiologist and surgeon about all of the medicines you are taking, especially any over-the-counter medicines such as aspirin or those that might contain aspirin. You should make a list of the medicines and bring it with you to the hospital.
It is always best to get complete instructions from your cardiologist and surgeon about the procedure, but here are some basics you can expect when you have valve repair or replacement surgery.
Before the Hospital Stay
Most patients are admitted to the hospital the day before surgery or, in some cases, on the morning of surgery.
The night before surgery, you will be asked to bathe to reduce the amount of germs on your skin. After you are admitted to the hospital, the area to be operated on will be washed, scrubbed with antiseptic, and, if needed, shaved.
A medicine (anesthetic) will make you sleep during the operation. This is called "anesthesia." Because anesthesia is safest on an empty stomach, you will be asked not to eat or drink after midnight the night before surgery. If you do eat or drink anything after midnight, it is important that you tell your anesthesiologist and surgeon.
If you smoke, you should stop at least 2 weeks before your surgery. Smoking before surgery can lead to problems with blood clotting and breathing.
Day of Surgery
 Before surgery, you may have an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), blood tests, urine tests, and a chest x-ray to give your surgeon the latest information about your health. You will be given something to help you relax (a mild tranquilizer) before you are taken into the operating room.
Before surgery, you may have an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), blood tests, urine tests, and a chest x-ray to give your surgeon the latest information about your health. You will be given something to help you relax (a mild tranquilizer) before you are taken into the operating room.
Small metal disks called electrodes will be attached to your chest. These electrodes are connected to an electrocardiogram machine, which will monitor your heart's rhythm and electrical activity. You will receive a local anesthetic to numb the area where a plastic tube (called a line) will be inserted in an artery in your wrist. An intravenous (IV) line will be inserted in a vein. The IV line will be used to give you the anesthesia before and during the operation.
After you are completely asleep, a tube will be inserted down your windpipe and connected to a machine called a respirator, which will take over your breathing. Another tube will be inserted through your nose and down your throat, into your stomach. This tube will stop liquid and air from collecting in your stomach, so you will not feel sick and bloated when you wake up. A thin tube called a catheter will be inserted into your bladder to collect any urine produced during the operation.
A heart-lung machine is used for all valve repair or replacement surgeries. This will keep oxygen-rich blood flowing through your body while your heart is stopped. A perfusion technologist or blood-flow specialist operates the heart-lung machine. Before you are hooked up to this machine, a blood-thinning medicine called an anticoagulant will be given to prevent your blood from clotting. The surgical team is led by the cardiovascular surgeon and includes other assisting surgeons, an anesthesiologist, and surgical nurses.
After you are hooked up to the heart-lung machine, your heart is stopped and cooled. Next, a cut is made into the heart or aorta, depending on which valve is being repaired or replaced. Once the surgeon has finished the repair or replacement, the heart is then started again, and you are disconnected from the heart-lung machine.\
The surgery can take anywhere from 2 to 4 hours or more, depending on the number of valves that need to be repaired or replaced.
Recovery Time
You can expect to stay in the hospital for about a week, including at least 1 to 3 days in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU).
Recovery after valve surgery may take a long time, depending on how healthy you were before the operation. You will have to rest and limit your activities. Your doctor may want you to begin an exercise program or to join a cardiac rehabilitation program.
If you have an office job, you can usually go back to work in 4 to 6 weeks. Those who have more physically demanding jobs may need to wait longer.
Minimally invasive heart valve surgery is a technique that uses smaller incisions to repair or replace heart valves. This means there is less pain. Minimally invasive surgery also reduces the length of the hospital stay and the recovery time.
Minimally invasive valve surgery can only be done in certain patients. This type of surgery cannot be done in patients
- With severe valve damage
- Who need more than one valve repaired or replaced
- Who have clogged arteries (atherosclerosis)
- Who are obese
In some cases, minimally invasive valve surgery can be done using a robot. Robotic surgery does not require a large incision in the chest. It is not available at all hospitals, and patients with severe valve damage cannot have the procedure. The Texas Heart Institute has a robot.
With robotic surgery, the surgeon has a control console, a side cart with 3 robotic arms, a special vision system, and instruments. A computer translates the surgeon's natural hand and wrist movements made on the control console to instruments that have been placed inside the patient through small incisions. The robot's controls can read even the tiniest of movements the surgeon makes.
Robotic surgery can reduce the time it takes to do valve surgery, as well as shorten the hospital stay and recovery time.
 Improving your quality of life and reducing angina and other CHD symptoms
Improving your quality of life and reducing angina and other CHD symptoms Allowing you to resume a more active lifestyle
Allowing you to resume a more active lifestyle Improving the pumping action of your heart if it has been damaged by a heart attack
Improving the pumping action of your heart if it has been damaged by a heart attack Lowering the risk of a heart attack (in some patients, such as those who have diabetes)
Lowering the risk of a heart attack (in some patients, such as those who have diabetes) Improving your chance of survival
Improving your chance of survival